In these reports, My teams and I completed a series of collaborative technical reports for the course Statistical and Data Mining Methods for Urban Data Analysis (MUSA 5000). Each project applied advanced statistical and machine learning techniques to real-world urban datasets, bridging spatial, socioeconomic, and behavioral insights for urban planning. These reports demonstrate my ability to perform rigorous data preparation, modeling, and spatial analysis using R and GeoDa, as well as to interpret quantitative results in policy-relevant contexts.
1. Using OLS Regression to Predict Median House Values in Philadelphia
(Co-authored with Krystal Won and Shuya Guan)
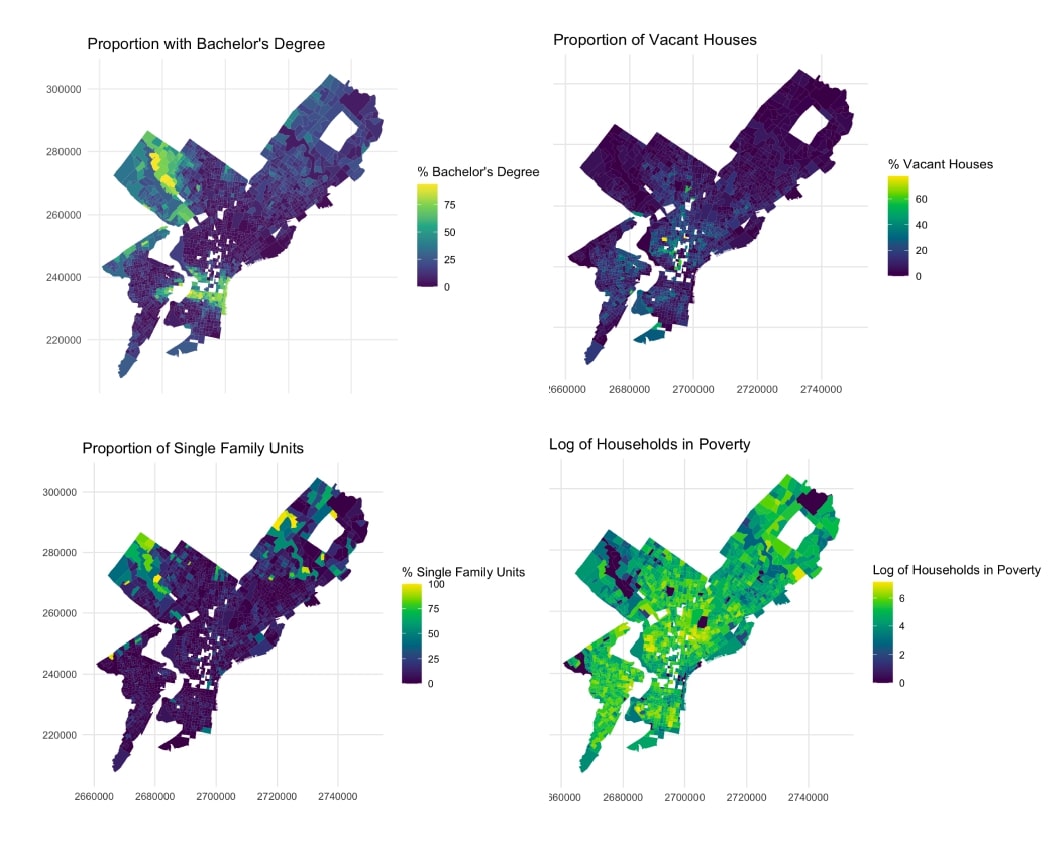
This report developed an Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression model to predict median house values across Philadelphia’s block groups using socioeconomic and housing indicators such as poverty rate, educational attainment, vacancy rate, and proportion of single-family homes. The study emphasized model diagnostics, regression assumptions, and validation through stepwise regression and cross-validation, providing an evidence-based understanding of neighborhood characteristics influencing property values.
2. Using Spatial Lag, Spatial Error, and Geographically Weighted Regression
(Co-authored with Shuya Guan and Yutong Jiang)
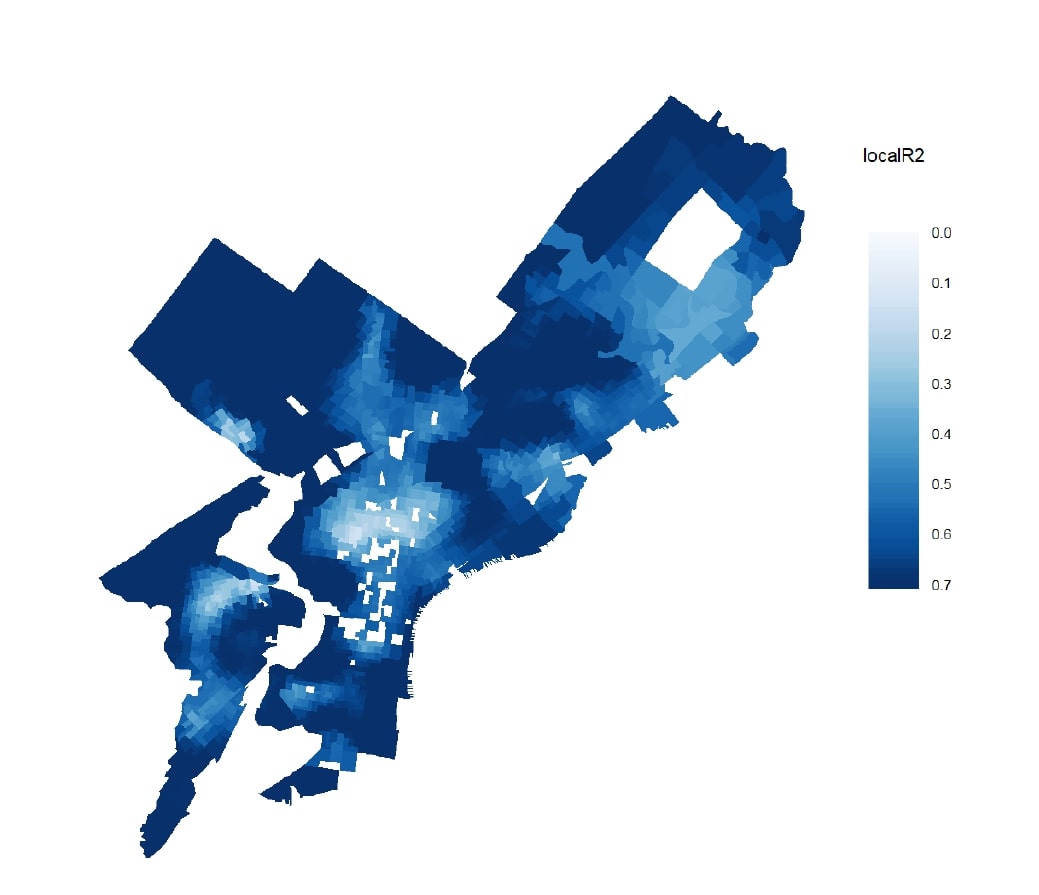
Building upon the first study, this report incorporated spatial regression models to address spatial autocorrelation in housing data. Using GeoDa, we compared spatial lag, spatial error, and geographically weighted regression (GWR) models to evaluate how spatial dependence shapes housing value patterns. The analysis highlighted the importance of accounting for neighborhood effects in urban housing markets and demonstrated improvements in model accuracy and interpretability.
3. Logistic Regression: Predictors of Alcohol-Related Car Crashes
(Co-authored with Shuya Guan and Yutong Jiang)
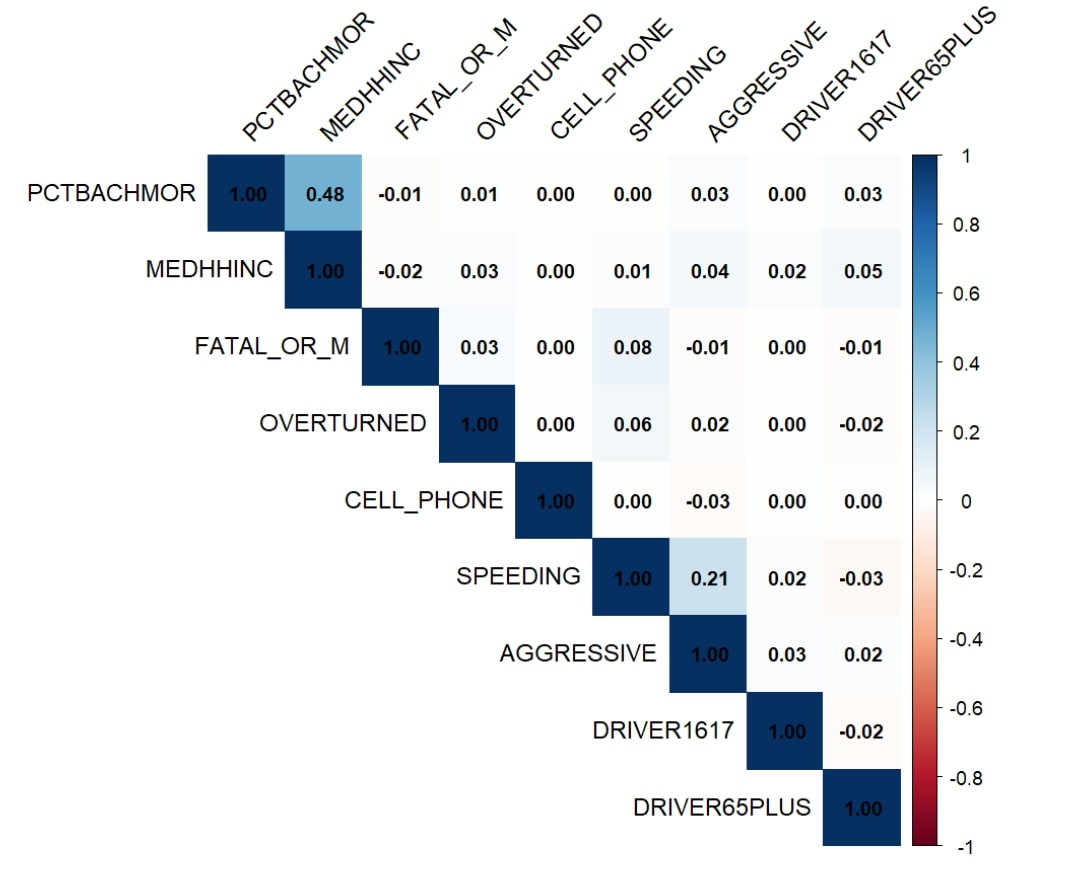
This project applied logistic regression to identify factors associated with alcohol-related traffic crashes in Philadelphia between 2008 and 2012. Variables such as driver age, speeding, and socioeconomic indicators were evaluated for their influence on crash likelihood. The study illustrated how logistic regression provides a robust framework for modeling binary outcomes and generated insights for traffic safety and policy interventions targeting impaired driving.
4. K-Means Clustering of Philadelphia Neighborhoods
(Co-authored with Shuya Guan and Yutong Jiang)
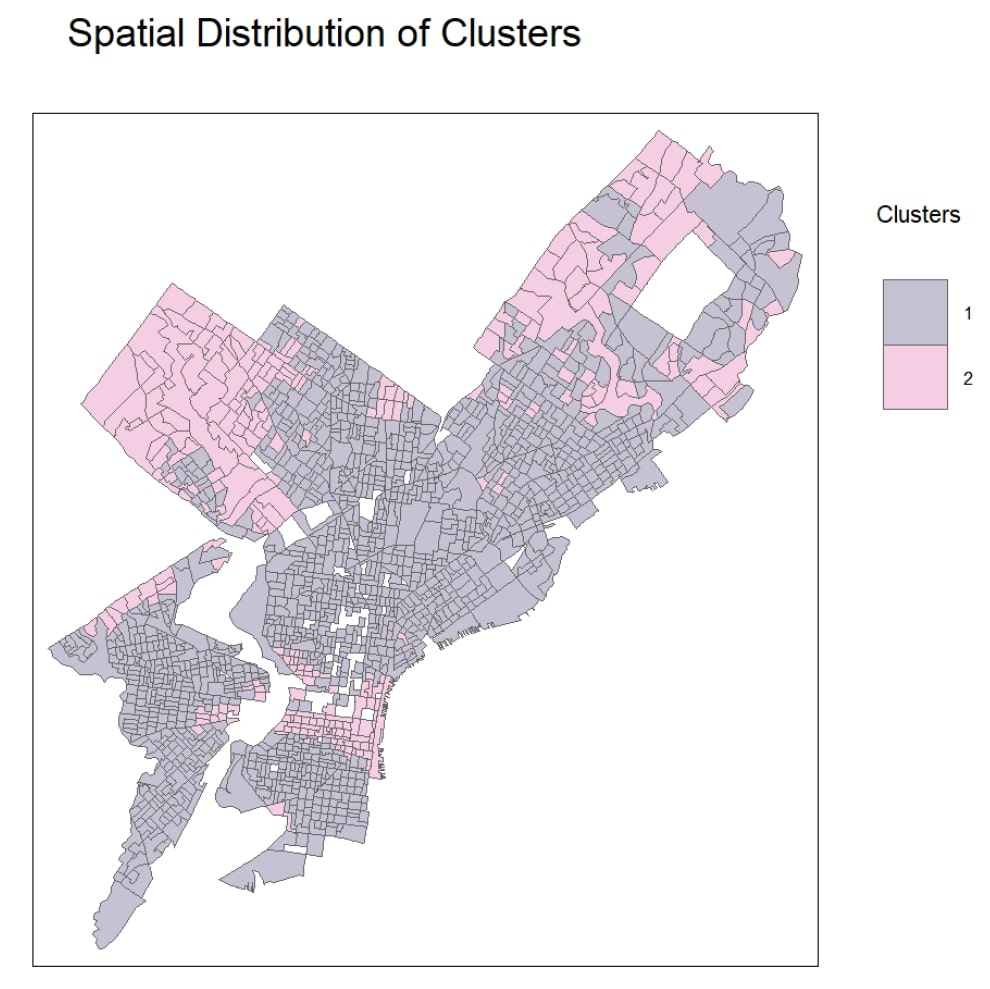
Using K-means clustering, this report categorized Philadelphia neighborhoods based on standardized socioeconomic and housing attributes, including income, education, vacancy, and housing type. The analysis identified natural groupings that reflect spatial and economic divisions across the city. Through iterative validation and visualization, the study demonstrated how clustering can uncover hidden patterns and inform data-driven neighborhood planning strategies.
5. Text Mining and Sentiment Analysis of IMDb Movie Reviews
(Co-authored with Shuya Guan and Yutong Jiang)
The final report explored sentiment analysis techniques in natural language processing using a dataset of 50,000 IMDb movie reviews. We analyzed the relationship between review length and emotional intensity using text cleaning, word frequency visualization, and lexicon-based sentiment scoring. The study showcased text mining as a tool for understanding public opinion and demonstrated transferable analytical skills beyond spatial and socioeconomic data.